Diffusion Transformer (DiT) Models
What is a Diffusion Transformer (DiT)? Diffusion Transformer (DiT) is a class of diffusion models that are based on the transformer architecture.
Introduction to Diffusion Models
Diffusion models are a type of generative model that simulates a Markov chain to transition from a simple prior distribution to the data distribution. The process is akin to a particle undergoing Brownian motion, where each step is a small random walk. This is why they are called “diffusion” models.
One of the key advantages of diffusion models is their ability to generate high-quality samples, which makes them particularly useful in tasks such as image synthesis.
Convolutional U-NET Architecture
The U-Net architecture is a type of convolutional neural network (CNN) , The architecture is designed like a U-shape, hence the name U-Net.
Vision Transformers
Vision Transformers (ViT) are a recent development in the field of computer vision that apply transformer models, originally designed for natural language processing tasks, to image classification tasks.
Understanding Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs)
Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) are a type of generative model that learn to generate data by modeling it as a diffusion process. This process begins with a simple prior, such as Gaussian noise, and gradually transforms it into the target distribution through a series of small steps
Shifting towards Transformer Backbone
Transformers, originally designed for natural language processing tasks, have shown great potential in computer vision tasks. Unlike convolutional networks, transformers can model long-range dependencies without the need for deep networks or large filters. This is because they use self-attention mechanisms, which allow each element in the input to interact with all other elements, regardless of their distance. Moreover, transformers are not translation invariant, which means they can capture the absolute position of features. This is achieved through the use of positional encodings, which add information about the position of each element in the input.
Diffusion Transformers (DiT)
DiT uses transformers in a latent diffusion process, where a simple prior (like Gaussian noise) is gradually transformed into the target image. This is done by reversing the diffusion process guided by a transformer network. An important aspect of DiT is the concept of diffusion timesteps. These timesteps represent the stages of the diffusion process, and the transformer network is conditioned on the timestep at each stage. This allows the network to generate different features at different stages of the diffusion process
Vision Transformers (ViT)
ViT uses transformers to directly generate the image in an autoregressive manner, where each patch is generated one after the other, conditioned on the previously generated patches. A key component of ViT is the use of adaptive layer norm layers (adaLN).
Scalability of DiT
Scalability is an important feature of Diffusion models with Transformers (DiT). As the size of the input data increases, the model should be able to maintain or improve its performance.
DiT Scaling Methods
There are two primary methods for scaling DiT models: scaling the model size and scaling the number of tokens.
Scaling Model Size
Scaling the model size involves increasing the complexity of the model, typically by adding more layers or increasing the number of neurons in each layer.
Scaling Tokens
Scaling the number of tokens involves increasing the size of the input data that the model can handle.
Diffusion Transformers Generalized Architecture
Spatial Representations
The model first inputs spatial representations through a network layer, converting spatial inputs into a sequence of tokens. This process allows the model to handle the spatial information present in the image data.
Positional Embeddings
Positional embeddings are a critical component of the transformer architecture. They provide the model with information about the position of each token in the sequence. This process helps the model understand the relative positions and relationships between different parts of the image.
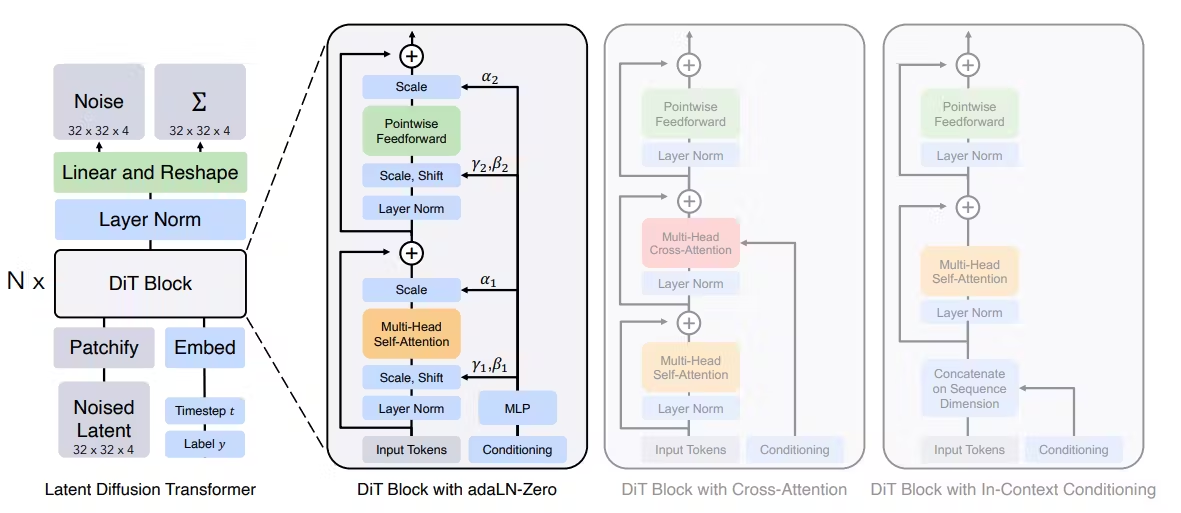
DiT Block Design
Stable Diffusion 3
Stable Diffusion 3 (SD3) is an advanced text-to-image generation model developed by Stability AI. SD3 combines a diffusion transformer architecture and flow matching.